Are you interested in finding 'rate of reaction homework'? You can find questions and answers on the topic here.
Table of contents
- Rate of reaction homework in 2021
- Rate of reaction worksheet grade 8
- Reaction rate constant
- Rate of chemical reaction
- Reaction rates and equilibrium worksheet answers
- Rate of reaction worksheet with answers
- Rate of reaction worksheet igcse
- Factors affecting rate of reaction worksheet pdf
Rate of reaction homework in 2021
 This image demonstrates rate of reaction homework.
This image demonstrates rate of reaction homework.
Rate of reaction worksheet grade 8
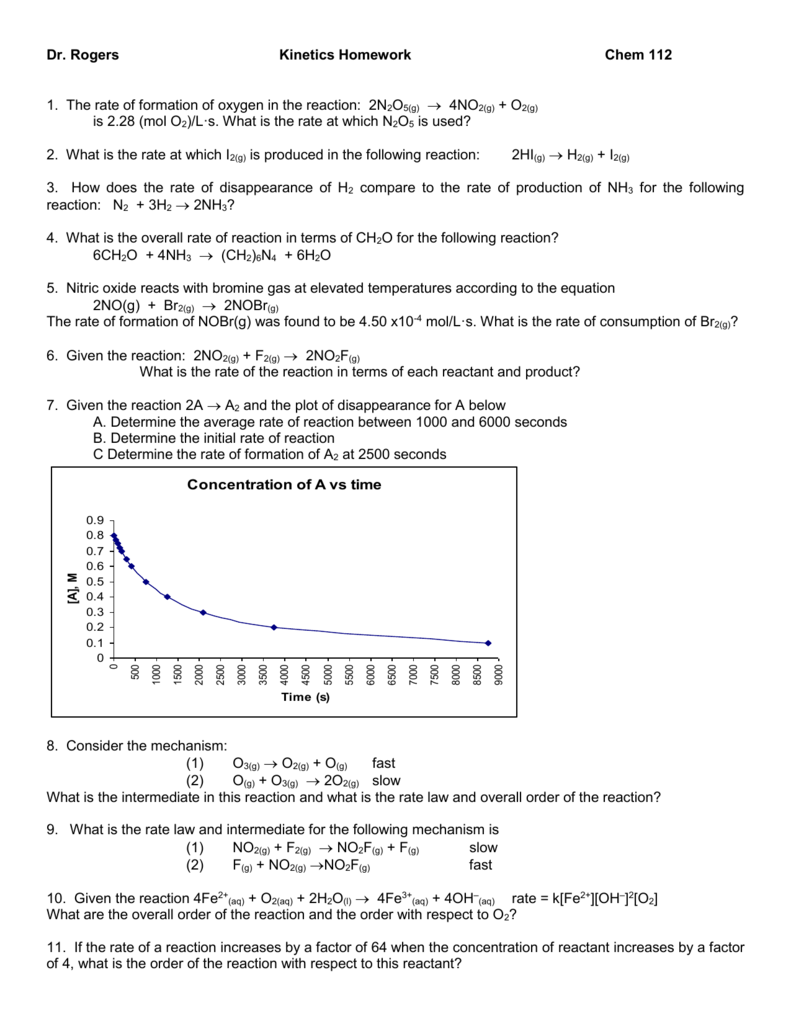 This picture shows Rate of reaction worksheet grade 8.
This picture shows Rate of reaction worksheet grade 8.
Reaction rate constant
 This picture demonstrates Reaction rate constant.
This picture demonstrates Reaction rate constant.
Rate of chemical reaction
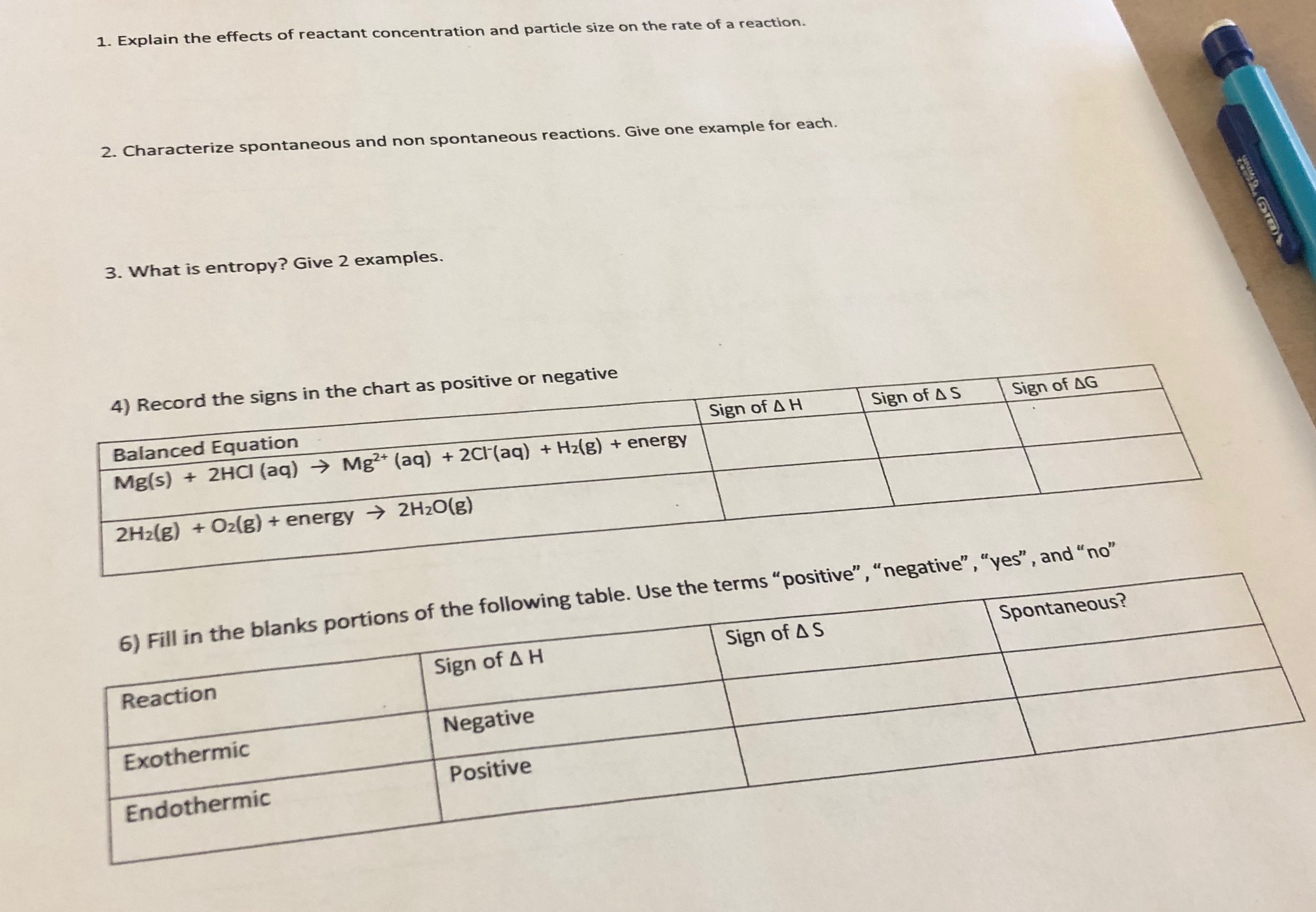 This picture shows Rate of chemical reaction.
This picture shows Rate of chemical reaction.
Reaction rates and equilibrium worksheet answers
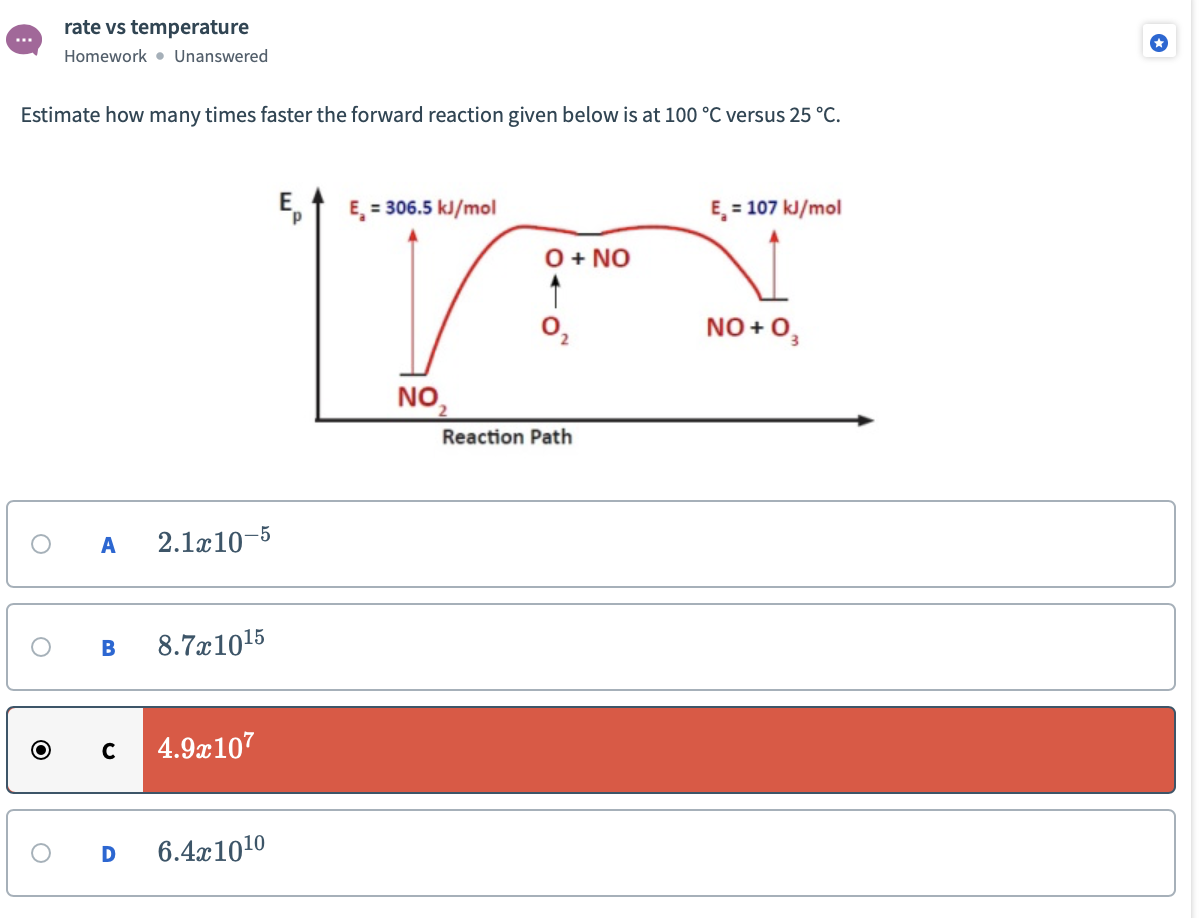 This image representes Reaction rates and equilibrium worksheet answers.
This image representes Reaction rates and equilibrium worksheet answers.
Rate of reaction worksheet with answers
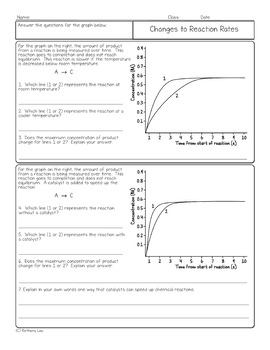 This picture representes Rate of reaction worksheet with answers.
This picture representes Rate of reaction worksheet with answers.
Rate of reaction worksheet igcse
 This image representes Rate of reaction worksheet igcse.
This image representes Rate of reaction worksheet igcse.
Factors affecting rate of reaction worksheet pdf
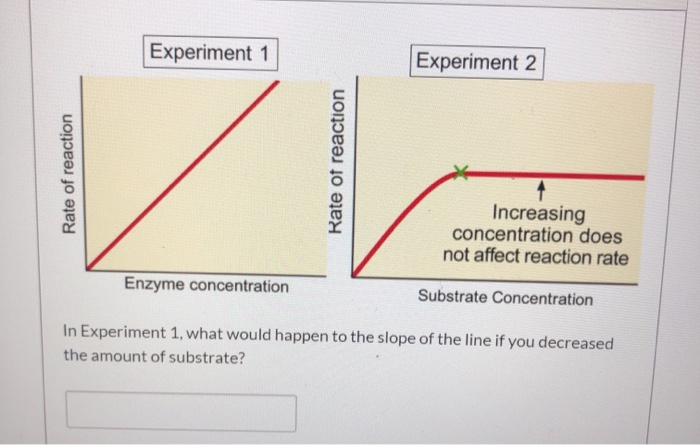 This picture illustrates Factors affecting rate of reaction worksheet pdf.
This picture illustrates Factors affecting rate of reaction worksheet pdf.
How to calculate the rate of a reaction?
There are different ways to determine the rate of a reaction. The method chosen usually depends on the reactants and products involved, and how easy it is to measure changes in them. The mean rate of reaction can be calculated using either of these two equations: [mean~rate~of~reaction = frac {quantity~of~reactant~used} {time~taken}]
How is the rate of reaction related to the activation energy?
The rate of a reaction is a measure of how quickly a reactant is used up, or a product is formed. Collision theory. For a chemical reaction to happen: A collision that produces a reaction is called a successful collision. The activation energy is the minimum amount of energy needed for a collision to be successful.
When is the change in mass of a reactant useful?
The change in mass of a reactant or product can be followed during a reaction. This method is useful when carbon dioxide is a product which leaves the reaction container. It is not suitable for hydrogen and other gases with a small relative formula mass, Mr. The units for rate are usually g/s or g/min.
How is the volume of a reaction measured?
Measuring volume. The change in volume of a reactant or product can be followed during a reaction. This method is useful when a gas leaves the reaction container. The volume of a gas is measured using a gas syringe, or an upside down burette or measuring cylinder. The units for rate are usually cm3 s-1 or cm3 min-1.
Last Update: Oct 2021